Detection of adulteration of Rhodiola rosea (L.) with other plant species
Formerly known by its more familiar name Rhodiola rosea L., Rhodiola is also called “golden root.” It grows in cold, mountainous regions. In Scandinavian countries, Rhodiola root has long been used to protect against and its the particularly stressful effects.
Properties and benefits of Rhodiola rosea L.
It is an antioxidant adaptogenic plant that helps the body adapt and protect cells during periods of physical and emotional stress. Rhodiola root extract helps reduce stress related fatigue or intense mental activity, and contributes to normal blood circulation. It is also linked to performance and intellectual responsiveness as well as optimal cognitive activity. Rhodiola root extract helps stimulate the nervous system and has beneficial effects on stress-induced fatigue and headaches, as well as on the cardiovascular system. It contributes to protecting the body from stress and helps maintain normal blood pressure.
Chemical activity of Rhodiola rosea L.
These effects are linked to the presence of specific substances such as rosavins (including rosavin, rosarin, rosine, and rosiridin), as well as salidroside and tyrosol. Dry extracts are also titrated for these molecules to ensure optimal quality. However, due to high demand, this plant is becoming increasingly rare and will become more difficult to source in the coming years. As a result, fraud is commonplace in an attempt to meet market demand.
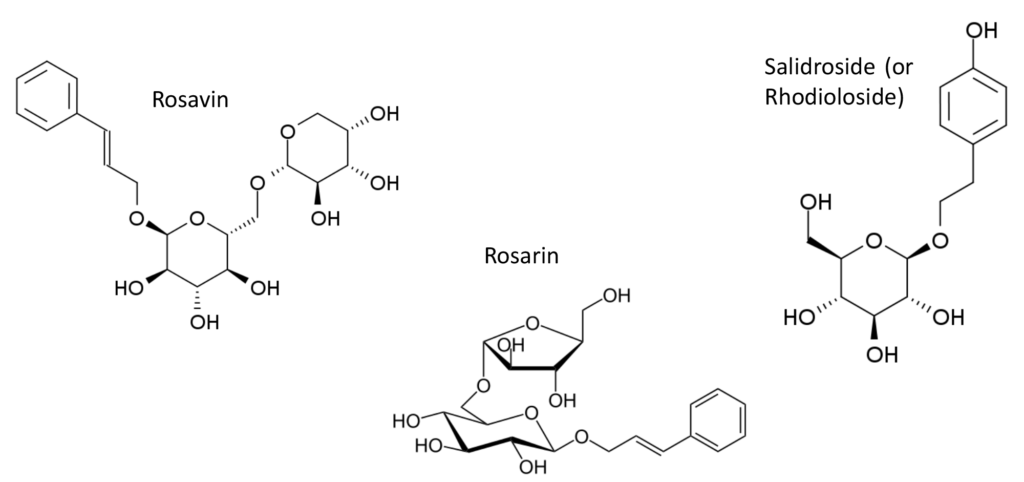
How to detect the adulteration of Rhodiola with other plant species
First of all, it is known that other species can be used in place of Sedum roseum, particularly Rhodiola crenulata (Hook.f. & Thomson) H.Ohba, which is known as the main adulterant. The absence of a monograph in pharmacopoeias means that internal methods must be used, and knowing the key features that differentiate Sedum roseum from other closely or distantly related plant species is crucial.
Examples of Rhodiola adulteration based on customer sample analyses
Each species has a distinct chemical profile. It is therefore essential to know what to expect from a typical profile of Sedum roseum (L.) Scop. root. In the various chemical profiles analysed, at BotaniCERT we have concluded that there are few compositional differences based on geographic origin (see Figure 2). In a campaign involving 74 commercial Rhodiola samples, 27 were identified as non-compliant with regard to the target species, representing 36% non-compliance. Among the various potential adulterants, Rhodiola crenulata (Hook.f. & Thomson) H.Ohba was the most frequently used in place of the intended species.
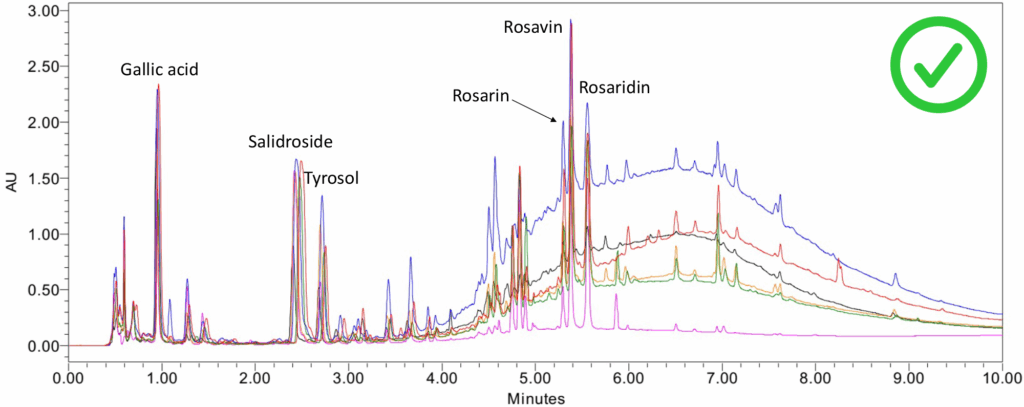
R. crenulata can be distinguished by the absence of rosavin derivatives, although it still contains high levels of salidroside and tyrosol. This species has significantly higher tannin content than S. roseum, particularly numerous gallate derivatives / esters of gallic acid (see Figure 3, compounds highlighted in blue). However, other species also contain rosavin derivatives, albeit in different proportions. Therefore, an analysis that focuses solely on these compounds is insufficient to reliably determine the plant species used to produce the extract.
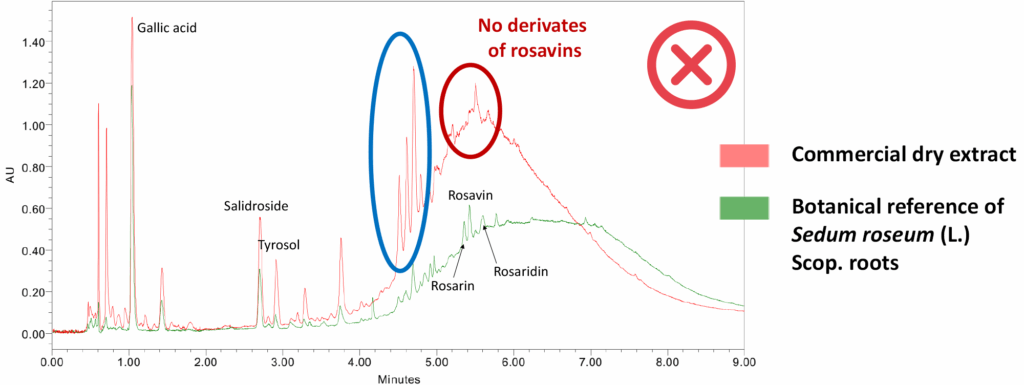
Proving the authenticity of Rhodiola through BotaniCERT testing
Rhodiola is a high-risk plant due to its complex sourcing and the numerous cases of fraud found on the market. Currently, the roots of Rhodiola crenulata (Hook.f. & Thomson) H.Ohba are frequently used to adulterate the target species, but fraud is evolving, and new types of adulteration will inevitably emerge. To effectively mitigate potential fraud, it is best to rely on the most comprehensive chemical profile possible, rather than on a single group of markers, which is often too restrictive to draw relevant conclusions.
Carrying out appropriate testing is essential for your plant-based products, particularly for extracts that are frequently adulterated.
How can you ensure the quality of your Rhodiola samples?
By performing an authentication adapted to dry extracts, and by confirming the presence of the target species, the absence of other plant species in the mixture, the absence of enrichment, and verifying the quantities of claimed active compounds.