How to detect it using other sources of flavonoids
The Ginkgo tree existed 200 million years ago. Today, it is said to be the oldest tree in the world.
Composition and properties of Ginkgo biloba L.
Its leaves contain high levels of flavonoids, particularly heterosides of quercetin, kaempferol, and isorhamnetin, which have potent antioxidant properties, especially active in the retina and the brain. The leaves also contain sesquiterpene lactones (bilobalide) and diterpene lactones (ginkgolides A, B, C, J), which act as inhibitors of PAF (platelet-activating factor). This anti-PAF activity, combined with the action of flavonoids, may explain many of Ginkgo’s properties, notably its role as a vascular regulator. Indeed, Ginkgo is known to improve capillary permeability and peripheral circulation. Like all commercially valuable plants, Ginkgo is a prime target for fraud, with counterfeiters becoming increasingly ingenious, especially in faking dry extracts.
Why Ginkgo biloba L. adulteration is possible
The flavonoids found in Ginkgo are all derivatives of quercetin, kaempferol, and isorhamnetin. These aglycones are common throughout the plant kingdom. Therefore, if the identity control of a Ginkgo dry extract relies solely on its polyphenolic profile, adulteration may often go undetected. The HPTLC (High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography) test used by the European Pharmacopoeia is based exclusively on polyphenolic substances, using chlorogenic acid and rutin as reference compounds. This means that if a fraudster adds another source of flavonoids to a Ginkgo sample, the adulteration will go undetected by this type of control.
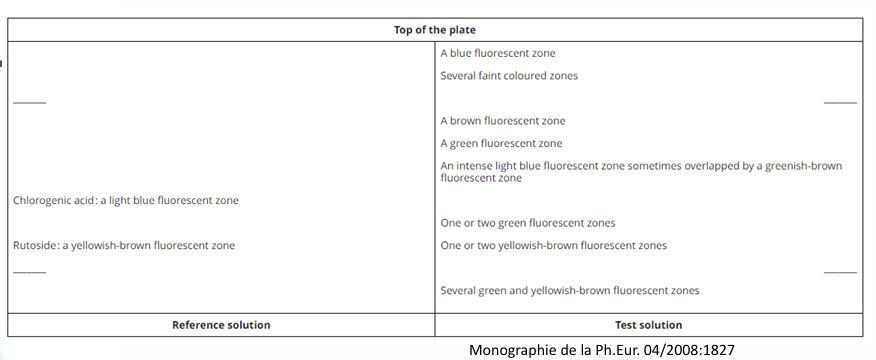
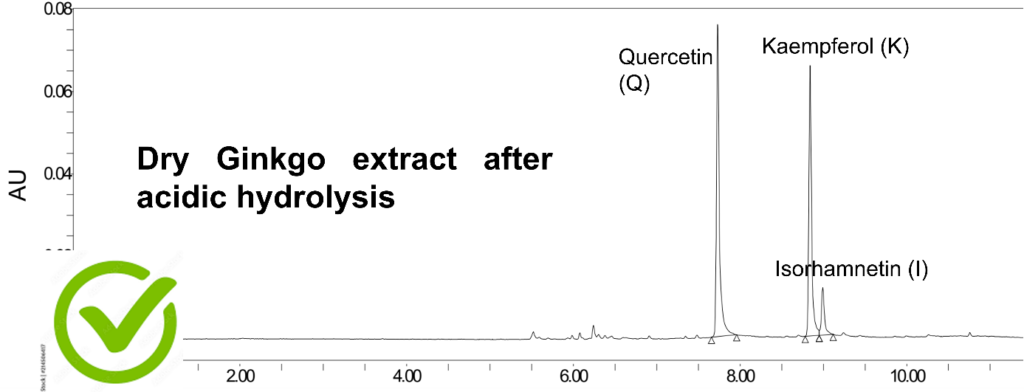
Ginkgo biloba adulteration examples through the analysis of client samples
All Ginkgo samples show the same proportion of heterosidic derivatives of the three above-mentioned aglycones (and shown in the adjacent chromatogram), which means that if a complete acid hydrolysis is performed on a Ginkgo dry extract, only the three aglycones will remain (as all heterosides will have lost their sugar moieties and appear as their respective aglycone forms).
If another source of flavonoids has been added, either additional aglycones may be detected, or the ratio between the three aglycones will be significantly different from the typical 1/1/0.1 ratio for Q/K/I (quercetin/kaempferol/isorhamnetin).
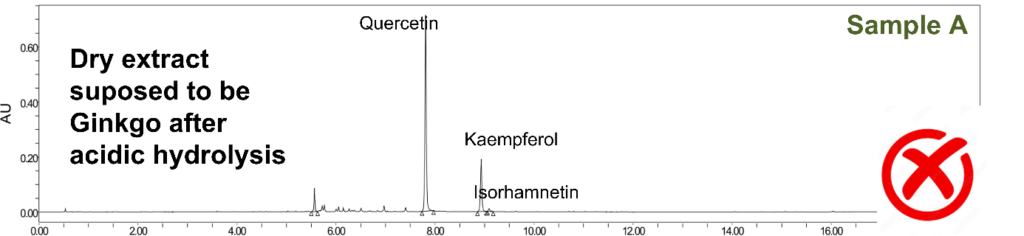
Adulteration of Ginkgo for sample A: dilution and addition
We find only the three aglycones, but quercetin is present in a higher quantity compared to the other two aglycones. The ratio here is closer to 4/1/0.1. Ginkgo is indeed present, but it has been diluted by at least 2 times, with the addition of a source of quercetin, most likely from an enrichment with an extract of floral buds of Sophora (Styphnolobium japonicum (L.) Schott).
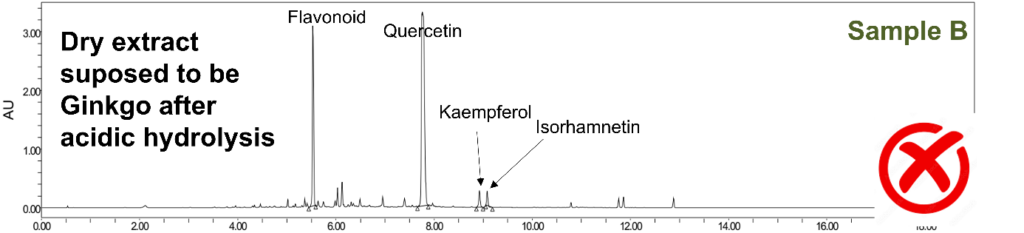
Adulteration of Ginkgo for sample B: absence or different species + addition
The flavonoid profile here is very different. It is not possible to confirm that the sample contains Ginkgo. Indeed, other flavonoids are present, and the ratio between kaempferol and isorhamnetin is significantly different from what is expected, suggesting that it is likely another species. However, quercetin is present in very large quantities, which could indicate that the extract has been further enriched with an extract of floral buds from Styphnolobium japonicum (L.) Schott.
Proving the non-adulteration of Ginkgo with BotaniCERT controls
Performing an inadequate control (based only on a few criteria) can be far more detrimental than not performing any controls at all. How can you ensure the quality of your Ginkgo samples? By proving the presence of Ginkgo, the absence of another plant species, the absence of any type of enrichment, and by verifying the quantities of active compounds.